Abstract
Introduction: As demonstrated in the phase II CHRONOS-1 trial, the pan-class I PI3K inhibitor copanlisib, with predominant activity against PI3K-α and PI3K-δ isoforms, is highly active (objective response rate [ORR] 59.2%) in the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory indolent B-cell lymphoma. At the time of the primary analysis (cutoff June 22, 2016; median safety follow-up of 24 weeks) the safety profile was characterized by low rates of severe elevated hepatic transaminases, diarrhea or inflammatory events, as well as low rates of opportunistic infections, fatal infections or other fatal serious adverse events. We conducted further safety and efficacy analyses based on a data cutoff on February 20, 2017 (8 months after the primary analysis) and the results are presented here.
Methods: Patients with histologically confirmed indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (4 subtypes: follicular [FL], marginal zone [MZL], small lymphocytic [SLL] and lymphoplasmacytoid/Waldenstrӧm macroglobulinemia [LPL-WM]) and relapsed after, or refractory to, ≥2 prior lines of treatment were eligible. Previous treatment had to include rituximab and an alkylating agent. Copanlisib was administered at a fixed dose of 60 mg via 1-hour I.V. infusion on an intermittent schedule days 1, 8 and 15 of a 28-day cycle. Treatment continued until progression or unacceptable toxicity. Objective tumor response rate (ORR) after ≥4 cycles was assessed per independent radiologic review (Cheson et al., JCO 2007). Secondary efficacy endpoints included duration of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Adverse events (AEs) were reported using MedDRA preferred terms (version 19.1). Prophylaxis for opportunistic infection was not mandated.
Results: The full analysis set comprised 142 patients, of whom 141 patients had indolent lymphoma (FL/MZL/SLL/LPL-WM: 104/23/8/6). Median age was 63 years (range 25-82). Prior treatment included a median of 3 (range 2-9) lines of therapy, with 61% being refractory to the last regimen. A total of 46 patients were receiving treatment at the June 2016 cutoff, of whom 25 remained on treatment as of Feb 2017. Five additional patients discontinued treatment due to AEs as of Feb 2017, for an overall total of 28.9%; discontinuation due to treatment-related AEs occurred in 18.3%. The median duration of treatment was 25.9 weeks (range 1-139) versus 21.9 weeks originally and the median duration of safety follow-up rose to 29.1 weeks (range 0.9-139.9), with 29.6% of patients followed for safety >1 yr.
Objective tumor responses were observed in 83 patients (ORR 58.5%) per independent central review compared to 84 (ORR 59.2%) in the June 2016 dataset. Notably, 3 additional complete responses (CR) were observed; 20 CRs in total (14.1%). Two of the additional CRs were in FL (16.4%) and 1 in MZL (13%). The median DOR was 12.2 months (range 0.03-28.1), while the median DOR was 20 months at primary evaluation. Median PFS was 11.3 months (range 0.03-30). Median OS had not been reached.
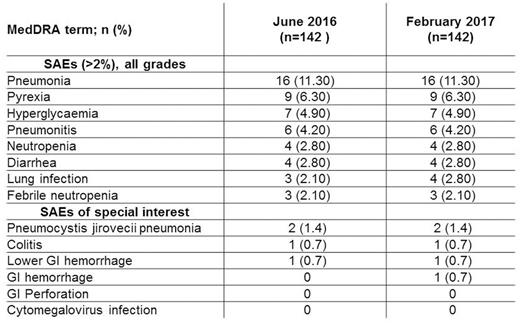
Worst-grade AEs and SAEs were mostly unchanged despite the longer safety follow up. Grade (G) 3/4 events were 52.8%/27.5% versus 52.8%/26.8% in June 2016, respectively. The most common treatment-emergent AEs (all-grade) included 49.3% transient hyperglycemia (48.6% in June 2016) and 29.6% transient hypertension (29.6% in June 2016). All-grade diarrhea was unchanged (33.8%), with 9 G3 events versus 8 in June 2016, with no G4 events reported. All-grade neutropenia was 27.5% (25.4% in June 2016), with G3/G4 9.2%/14.1% (8.5%/13.4% in June 2016). SAEs were observed in 74 (52.1%) patients versus 71 (50%) in June 2016, but individual SAEs occurring in ≥3 (>2%) patients were low (see Table). There were no new treatment emergent mortality; 6 overall, 3 treatment-related.
Conclusions: Updated analyses based on a data cut-off of Feb 2017 reaffirmed the robust efficacy (ORR of 58.5% and median DOR >1 year) of copanlisib treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent B-cell lymphoma. Similarly, the low rate of individual severe toxicities overall and the lack of late-onset toxicities with long term follow up (29.6% with >1 year) suggests that intermittent IV dosing may contribute to the favorable safety profile for copanlisib.
Dreyling: MorphoSys AG: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Sandoz: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Santoro: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Leppa: Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen Cilag: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding. Lenz: Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kim: Roche: Research Funding; Kyowa-Kirin: Research Funding; Donga: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; J&J: Research Funding; Celltrion, Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding. Morschhauser: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy. Ishida: Bayer SA: Employment. Lu: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Hiemeyer: Bayer AG, Pharmaceuticals Division: Employment. Miriyala: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Garcia-Vargas: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Childs: 11. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Zinzani: Bayer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Johnson & Johnson: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Verastem: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal